We help the world since 2012

8 Common Mobile Robots and Their Application Scenarios
Today we are going to talk about the commn mobile robots. First, we have to understand what is the mobile robot. A few days ago, we have written the blog with the topic “What’s a robot ?”
What’s mobile robot ?
A mobile robot is a machine that performs work automatically. It can be directed by a human being, it can run pre-programmed routines, and it can act according to a program of principles developed with artificial intelligence technology. Its task is to assist or replace human work, such as production, construction, or hazardous work.
From Wikipedia, the mobile robot is defined as “A mobile robot is an automatic machine that is capable of locomotion.[1] Mobile robotics is usually considered to be a subfield of robotics and information engineering.”
I am sure you have a basic understanding of mobile robotics. As we all know, mobile robots have become indispensable technological devices in today’s era of industrial automation and intelligence. They are not only able to dramatically improve productivity, but also solve many complex logistics, manufacturing and service problems.
There are 8 common types of mobile robots on the market with Robot Application Scenarios as follows:
8 common mobile robots and their application scenarios
1. Wheeled Mobile Robots

Characteristics: Wheeled mobile robots are driven by wheels, and are the most common and popular type of mobile robots. Since wheels can move efficiently and quickly on flat surfaces, they have high speed and energy efficiency, and are suitable for applications that require high speed. They have a relatively simple structure, are easy to control and maintain, and offer a high degree of flexibility.
Application scenarios: Wheeled mobile robots are widely used in many fields such as industry, logistics, service and household. For example, AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) are commonly used for material handling in warehouse logistics systems, while AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) are responsible for distribution tasks in factories or supermarkets.
Examples: AGVs, AMRs, service robots such as Pepper.
2. Tracked Mobile Robots (CMR)

Characteristics: Tracked Mobile Robots use tracks instead of wheels to move around, and have strong off-road capabilities, allowing them to travel on uneven ground or complex terrain. Compared with wheeled robots, tracked robots have better grip and stability, and are able to perform tasks in mud, snow, sand and other environments.
Application Scenario: Tracked mobile robots are widely used in the military, such as combat robots and unmanned tanks, capable of crossing obstacles on the battlefield. They are also commonly used in rescue missions, capable of searching for survivors in disaster areas or earthquake rubble.
Examples: combat robots, remotely operated unmanned tanks, expeditionary robots.
3. Legged Mobile Robots

Characteristics: Legged Mobile Robots walk by mimicking the gait of animals, and usually have four, six, or more feet to adapt to a variety of complex terrain. Although they move slower than wheeled or tracked robots, they are able to maintain stable movement over uneven terrain. Footed robots also have the ability to balance on unbalanced surfaces, such as sand, stairs, and rocks.
Application Scenarios: Footed robots have great potential for rescue missions, scientific research, and exploration of complex terrain. For example, Boston Dynamics’ Spot is used in areas such as building inspection and security patrols, while humanoid robots are capable of more complex human activities.
Examples: Spot, a quadrupedal robot; Atlas, a humanoid robot.
4. Snake Mobile Robots

Characteristics: Snake Mobile Robots mimic the movement of a snake through flexible joints and are able to slither through tight spaces. They typically consist of multiple small joints and modules that allow them to maneuver into areas that are inaccessible to humans or traditional machines. Snake robots are highly adaptable and suitable for performing tasks in complex, narrow and winding environments.
Application Scenario: Snake mobile robots excel in areas such as post-disaster search and rescue and pipeline inspection. They can enter narrow crevices obstructed by collapsed buildings for searching, and can also be used for complex medical probes and surgeries.NASA’s EELS program develops serpentine robots for space exploration.
Examples: NASA’s EELS serpentine robot, pipeline inspection robot.
5. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs)

Characteristics: Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, or drones, fly through the air by means of rotary or fixed wings. UAVs usually have the ability to fly autonomously or be remotely maneuvered to cover a wide area. They are able to realize aerial monitoring, data collection and other functions by carrying cameras, sensors and other equipment, and are not restricted by ground conditions.
Application Scenario: UAVs are widely used in many fields such as logistics, agriculture, rescue, and military. For example, in the field of logistics, companies such as Amazon and Shunfeng have begun to use UAVs for aerial distribution of small packages; in agriculture, UAVs can be used for crop monitoring, pest control and pesticide spraying; and in rescue missions, UAVs are capable of quickly scouting the disaster area.
Examples: quadcopter drones, fixed-wing drones.
6. Underwater Robots (AUV/ROV)
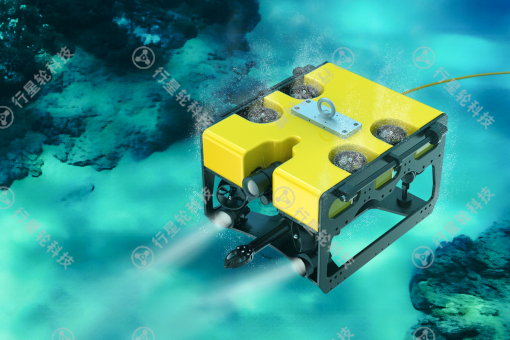
Characteristics: Underwater robots are robots specifically designed for underwater environments and are categorized as Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) and Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs).AUVs can perform tasks autonomously, while ROVs are usually controlled by an operator via remote control. They can perform a variety of tasks in underwater environments, such as ocean exploration, deep-sea mining, and maintenance of undersea equipment.
Application Scenario: Underwater robots are widely used in marine scientific research, oil and gas exploration, military reconnaissance and other fields. For example, in deep-sea exploration, underwater robots can be used to collect ocean data, inspect seafloor topography, or repair seafloor equipment. rovs are often used to inspect and repair underwater oil rigs and pipelines.
Examples: remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), deep-sea exploration robots.
7. Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robots
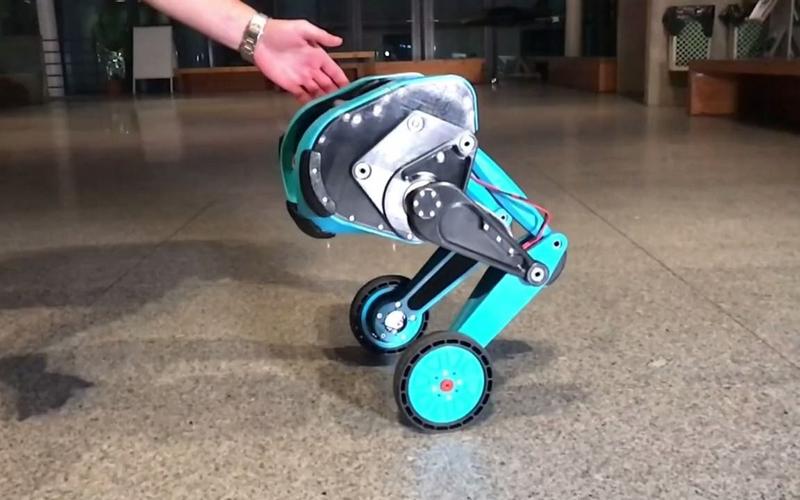

Characteristics: Two-Wheeled Self-Balancing Robots rely on built-in gyroscopes and sensors to maintain balance, and usually have only two wheels. These robots are designed to be flexible and able to move freely in tight spaces and remain stable on slopes and uneven surfaces. These robots are often used for short-distance mobility or light cargo transportation.
Application Scenario: Two-wheeled balancing robots are widely used in personal transportation and service robotics. For example, Segway and other balance bike robots are used for short-distance transportation; some hotels and office buildings use two-wheeled balance robots to provide delivery services.
Examples: Segway, balancing robots, delivery robots.
8. Rail-Guided Robots

Characteristics: Rail-Guided Robots move along a pre-determined track or path and are typically used to perform highly repetitive and precise tasks. Because they always move along a fixed route, rail-guided robots offer high precision and stability and are often used in production lines and warehouse management systems that require a high degree of automation.
Application Scenario: Orbital robots are widely used in automated factory production lines, warehouse management and medical device delivery. In automated factories, orbital robots can efficiently transfer products from one station to another; in the medical field, orbital robots are used to convey medicines and medical equipment.
Examples: automatic production line transfer robots, hospital logistics orbital robots.
If you are looking for high-performance modular power supplies for mobile robots or Robot Technology, please contact CHONDATECH. We specialize in providing power supply solutions for a wide range of mobile robots to meet the needs of different application scenarios since 2012.




